Degree Day Overview
First available in Inventory Services: 2018.3
A degree day is used to estimate fuel consumption for a particular location based on historical and predicted weather data. This estimation allows you to forecast orders for heating fuels, anticipating your customers' needs ahead of actual demand.
-
Degree Day is a cloud-based forecaster. You access degree day information in these three windows:
-
Degree Day Vendor Keys
-
Location Setup
-
Degree Day Site Review
In these windows, you can:
-
Set up access to third-party weather forecasting services that provide forecast data
-
View, set up, and manage information on the customers or locations that will be receiving the fuel order
-
View projected degree day readings and corresponding projected orders
-
View forecasted and historical temperature entries for each customer or location
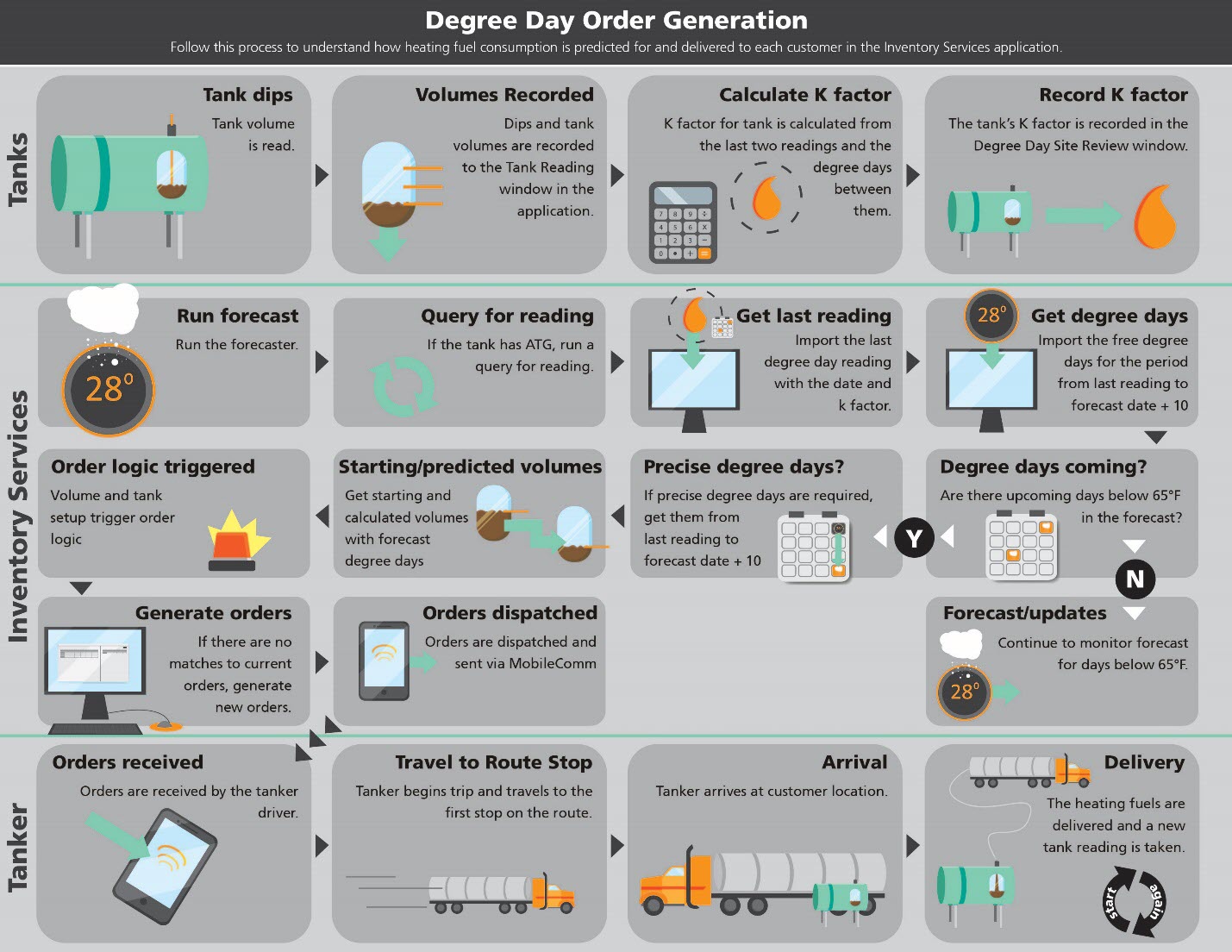
Understanding the calculations used to find a degree day and estimate fuel consumption
These calculations can be used to estimate the fuel level of a tank without actually reading the tank, allowing for off-site management of your customers' product needs.
| If a tank has an automatic gauge that provides on-demand readings, degree day calculations are not necessary. |
Degree day
Degree days are a measure of how much (in degrees), and for how long (in days), the outside air temperature was below a certain level at a location. They are commonly used in calculations relating to the energy consumption required to heat buildings. You calculate a degree day by subtracting the average temperature of one 24-hour period from the median temperature of 65° F.
K factor
A K factor is the numerical value of the fuel consumption per degree per day per location. Simply put, it is the burn factor value for each location or tank. K factor is calculated by dividing the volume of fuel consumed from a tank over a period of time by the number of degree days per period.